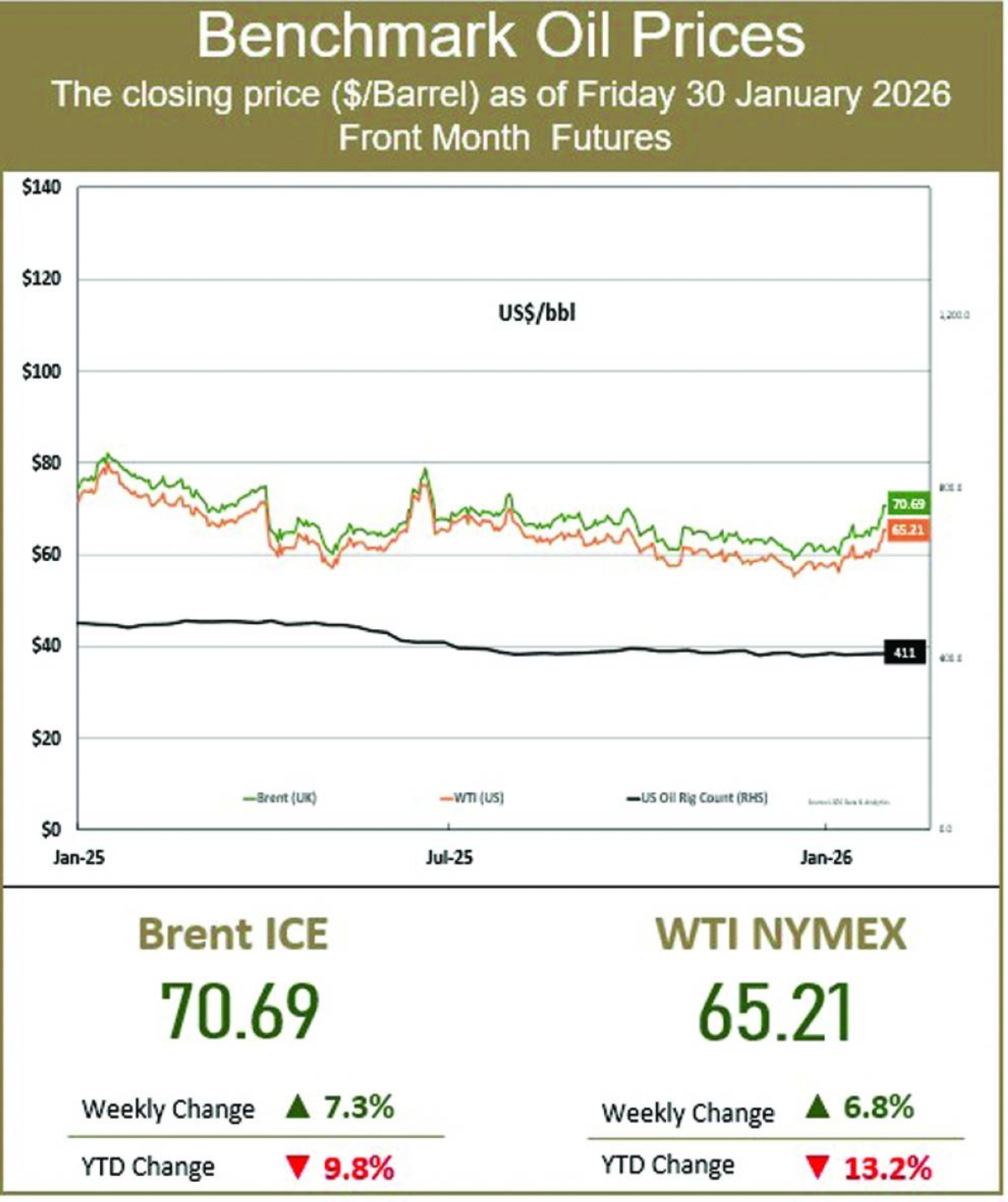
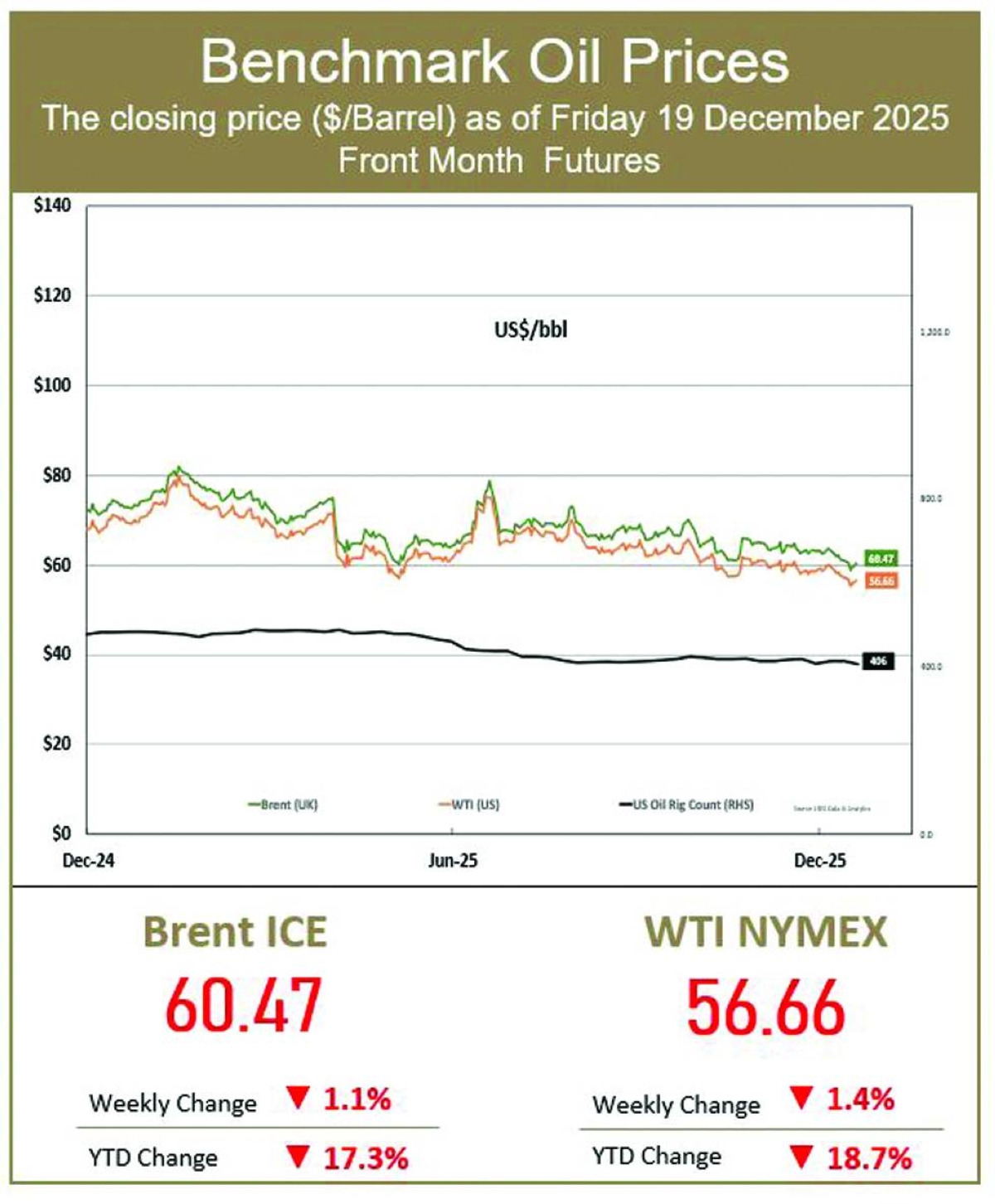
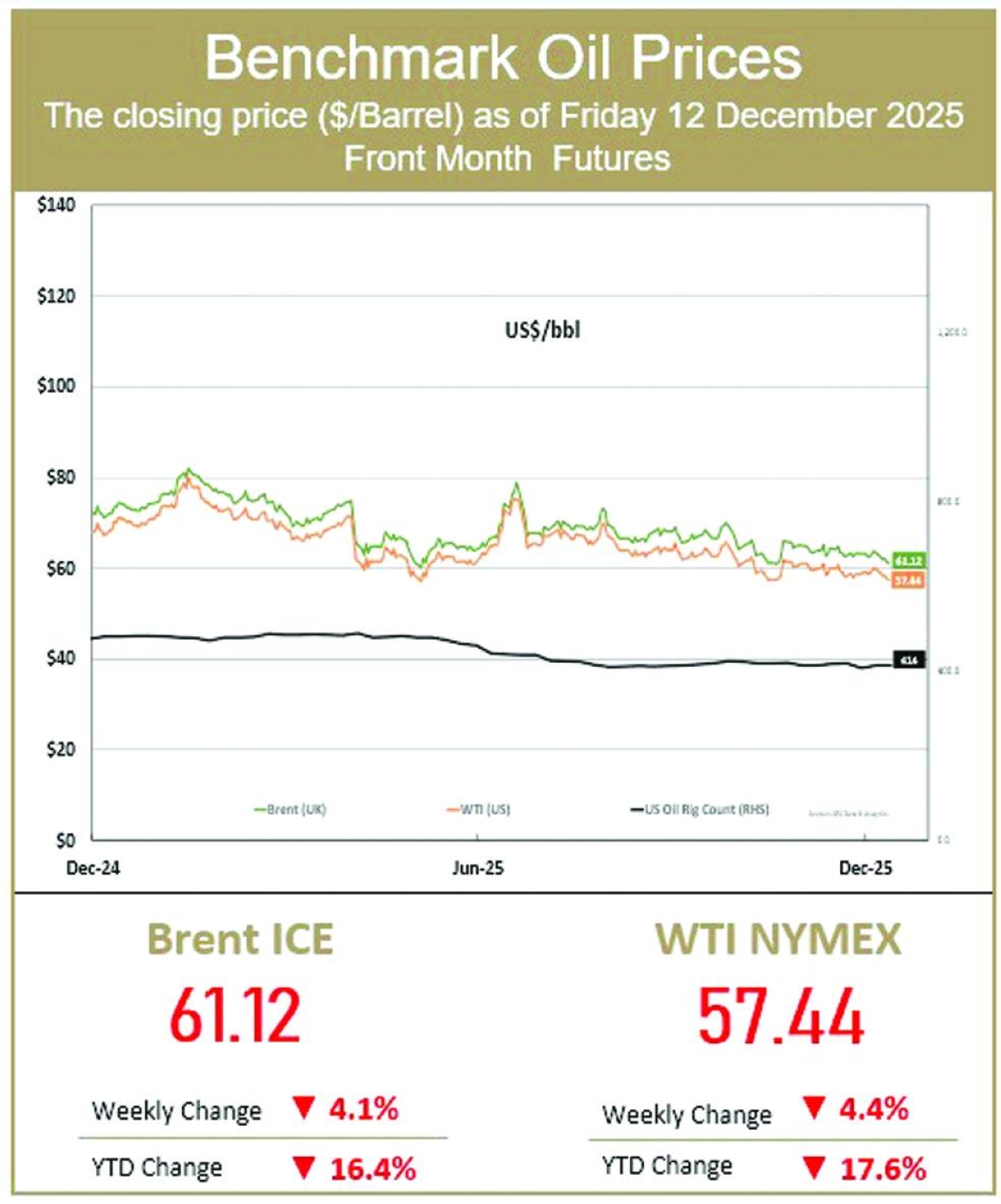
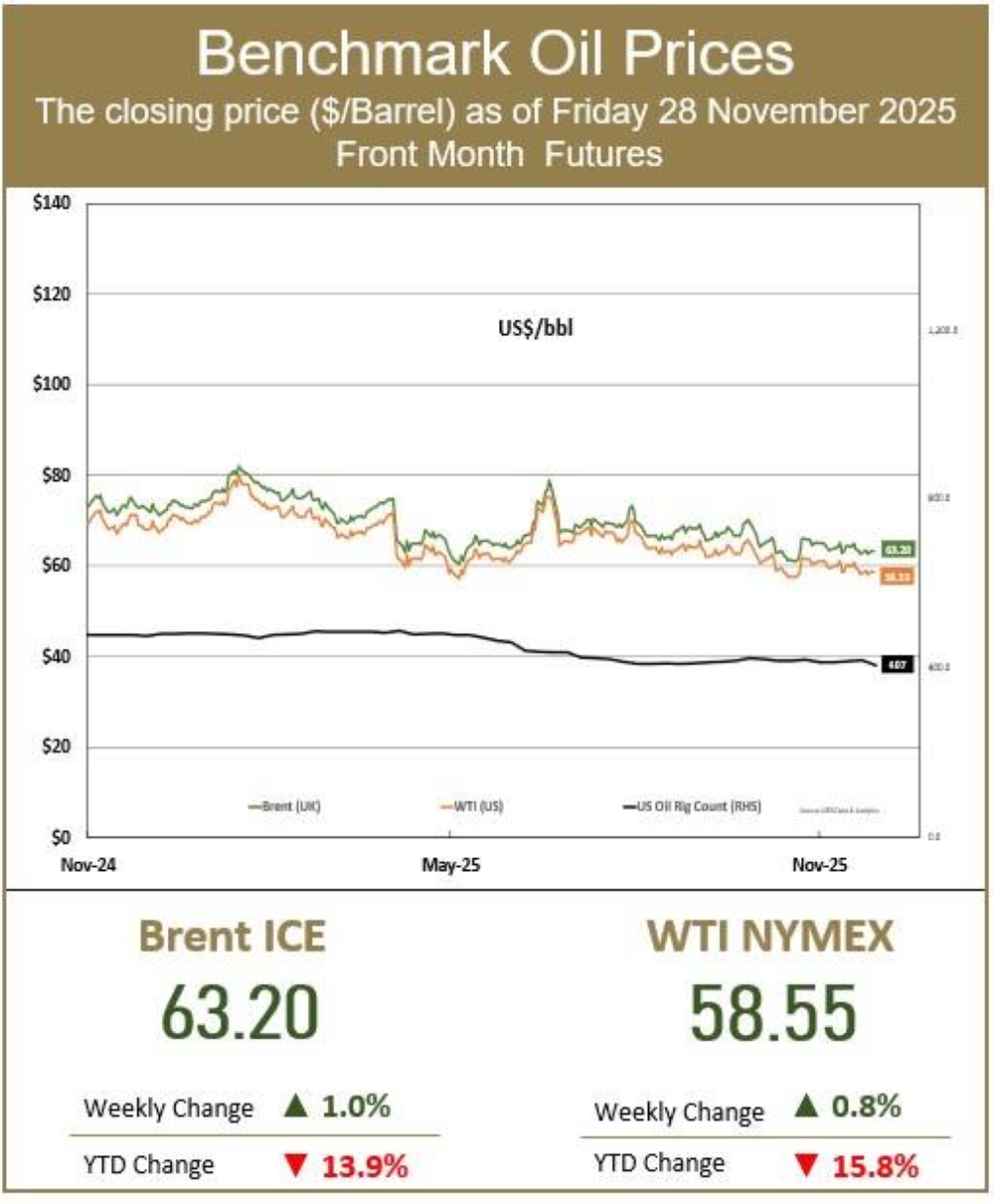
British oil giant BP announced Tuesday an 86% slide in annual net profit, hit by lower crude prices and a huge write-down linked to its green energy transition.Profit after tax dropped to $55mn last year from $381mn a year earlier, BP said in a statement.The results come ahead of Meg O'Neill taking over as BP's chief executive in April, becoming the first woman to lead an oil major.BP said the annual results included an impairment totalling around $4bn linked to its "transition businesses in the gas and low carbon energy segment".It added that its annual performance was "delivered against a weaker oil price environment".Underlying earnings, which strip out some energy-price movements and one-off charges, fell 16% to $7.5bn last year.Energy prices have been under pressure on concerns that US President Donald Trump's tariffs will crimp economic growth.They dropped further as a result of higher output by Opec+ nations and hopes of an end to the war in Ukraine, as Russia remains a major energy producer.More recently, prices have risen as Trump ramped up military threats against Iran, but have since cooled on easing tensions between Washington and Tehran.The international oil price benchmark, Brent North Sea crude, was steady Tuesday at $69 per barrel.BP's boardroom shakeup at the end of last year came with the company pivoting back to its more profitable oil and gas business, slashing clean energy investment after shelving targets on reducing carbon emissions.Carol Howle has served as interim CEO since Murray Auchincloss unexpectedly stepped down in December."We look forward to Meg O'Neill joining as CEO in April as we accelerate our progress to build a simpler, stronger and more valuable BP for the future," Howle said in the statement."We are in action and we can and will do better for our shareholders," she added as the group suspended share buybacks.O'Neill, an American who spent 23 years working for ExxonMobil, is the first external candidate to be appointed CEO of BP in the group's 116-year history.She has led Australian group Woodside Energy since April 2021.BP, which is not alone among peers in scaling back climate targets, agreed in December to sell a majority stake in its Castrol lubricants business to US investment firm Stonepeak for $6bn, as it seeks to cut debt. KeringFrench luxury group Kering reported Tuesday a steep fall in net profit but forecast a return to growth as sales declines were stanched at Gucci and other key brands.The group, which embarked on a deep restructuring effort with the hiring of CEO Luca de Meo last year, also posted lower debt and announced an exceptional dividend payout."The group's 2025 performance does not reflect its true potential," De Meo, who was poached from Renault, said in a statement."We have seen signs of a rebound on the market" in the third quarter, which "lets us begin 2026 with optimism", he later told a press conference.Kering has struggled to turn things around at Gucci, its flagship Italian fashion house famous for its handbags, in recent years, and in March it wooed Georgian designer Demna to take over as artistic director.Overall sales dropped by 13% to 14.7bn euros ($17.5bn) last year while net profit plunged by 93.6%, Kering said, reflecting the steep losses at Gucci and Yves Saint Laurent, by far its biggest brands.But the sales performance improved in the fourth quarter, when like-for-like revenue at Gucci fell 10% to 1.6bn euros -- compared with quarterly declines of around 25% for much of last year.This year "will be the year when Kering starts to reconquer its territory", De Meo said, with around 150 stores to be closed, a third of them Gucci boutiques, mainly in Asia and to a less extent the United States."That doesn't mean we're not going to open new stores" he said, adding that his goal was to avoid loss-making stores. BarclaysBritish bank Barclays said Tuesday that its net profit rose 16% last year, helped by income growth at its investment division as US President Donald Trump's tariffs blitz caused volatility in markets.Profit after tax climbed to £6.2bn ($8.4bn) from £5.3bn in 2024, Barclays said in a statement.Total income grew nine percent to £29.1bn year on year. Its investment bank saw income rise 11% to £13.1bn.Setting a new performance target, chief executive CS Venkatakrishnan said the bank aimed "to secure sustainably higher returns through to 2028 and beyond" thanks to improved efficiency measures and "harnessing new technology, including AI".He added that the bank plans to return more than £15bn in capital distributions to shareholders through to 2028."Barclays has put in a strong showing, beating profit expectations, posting a firmer capital position and lifting its longer-term targets above market forecasts," said Matt Britzman, an equity analyst at Hargreaves Lansdown."Top-line performance was led by US card spending and a solid investment banking performance," he added.Sharp fluctuations in financial markets last year were exacerbated by Trump's announcement of sweeping tariffs on global trading partners, which were later scaled back, driving up volumes of financial transactions.Since then, countries have reached trade deals with Washington to lower the levies, but uncertainty over the economic impact has remained.Offsetting last year's gains, Barclays suffered a £110mn hit last year from exposure to a US subprime auto lender, Tricolor, whose collapse spooked investors.Barclays has meanwhile set aside £325mn in compensation payments after some UK car loans were deemed unlawful.That is far less than an impairment of £1.95bn from British rival Lloyds, whose net profit grew to £4.8bn last year.The UK Supreme Court last year mostly overturned judgements made by the Court of Appeal that ruled it was unlawful for car dealers to receive a commission on loans without sufficiently informing borrowers. PhilipsDutch electronics and medical device manufacturer Philips said Tuesday it had bounced back into the black in 2025, as it seeks to turn the page on a scandal over faulty sleep apnoea machines.Philips posted a profit of 897mn euros last year, after three straight years of losses."We strengthened our company while navigating a dynamic macro environment. We ended the year with strong, robust margin expansion despite tariffs," chief executive Roy Jakobs said in a statement.The profit came in above the consensus forecast of analysts polled by the company of 775mn euros.Once famous for making lightbulbs and televisions among other products, Amsterdam-based Philips in recent years has sold off subsidiaries to focus on medical care technology.It posted overall sales of 17.8bn euros in 2025, compared to the 18.0bn euros it banked in 2024. Analysts' consensus forecast was for sales of 17.7bn. AstraZenecaBritish pharmaceutical giant AstraZeneca said Tuesday that its net profit jumped 45% last year on strong sales of cancer drugs, as it expands its reach in the United States and China.Profit after tax rose to $10.2bn in 2025 from $7.0bn a year earlier, AstraZeneca said in a statement.Revenue increased nine percent to $58.7bn, boosted by a rise in cancer drug sales."In 2025, we saw strong commercial performance across our therapy areas and excellent pipeline delivery," chief executive Pascal Soriot said in an earnings statement."The momentum across our company is continuing in 2026," he added.Soriot later told reporters he was "very confident" the company would achieve its target of $80bn in annual revenue by the end of the decade."If AstraZeneca knocks it out of the park with its current pipeline of final-stage trials, it could stand head and shoulders above the peer group," said Dan Coatsworth, head of markets at AJ Bell.AstraZeneca has recently expanded its footprint into its two largest markets, the United States and China.The group said last month that it would invest $15bn in China through 2030 to expand its medicines manufacturing and research, as UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer made a trip to Beijing.During the visit, it also announced a deal with Chinese group CSPC Pharmaceutical to help develop and market weight-loss injections, which have exploded in popularity in recent years.Britain's largest drugmaker has also been making a recent shift towards the United States, which it hopes will account for half its global revenue by 2030.Last year, the US accounted for 43% of its total revenue.Highlighting the increasing importance of the US market, AstraZeneca began listing its shares directly on the New York Stock Exchange in February to attract more investors.It will remain headquartered in the UK and keep its primary share listing in London.Faced with US President Donald Trump's threats of pharmaceutical tariffs, AstraZeneca in July revealed plans to invest $50bn by 2030 on boosting its US manufacturing and research operations.Trump also forged a deal with AstraZeneca for significantly lower drug prices in the United States.
Friday, February 13, 2026
|
Daily Newspaper published by GPPC Doha, Qatar.