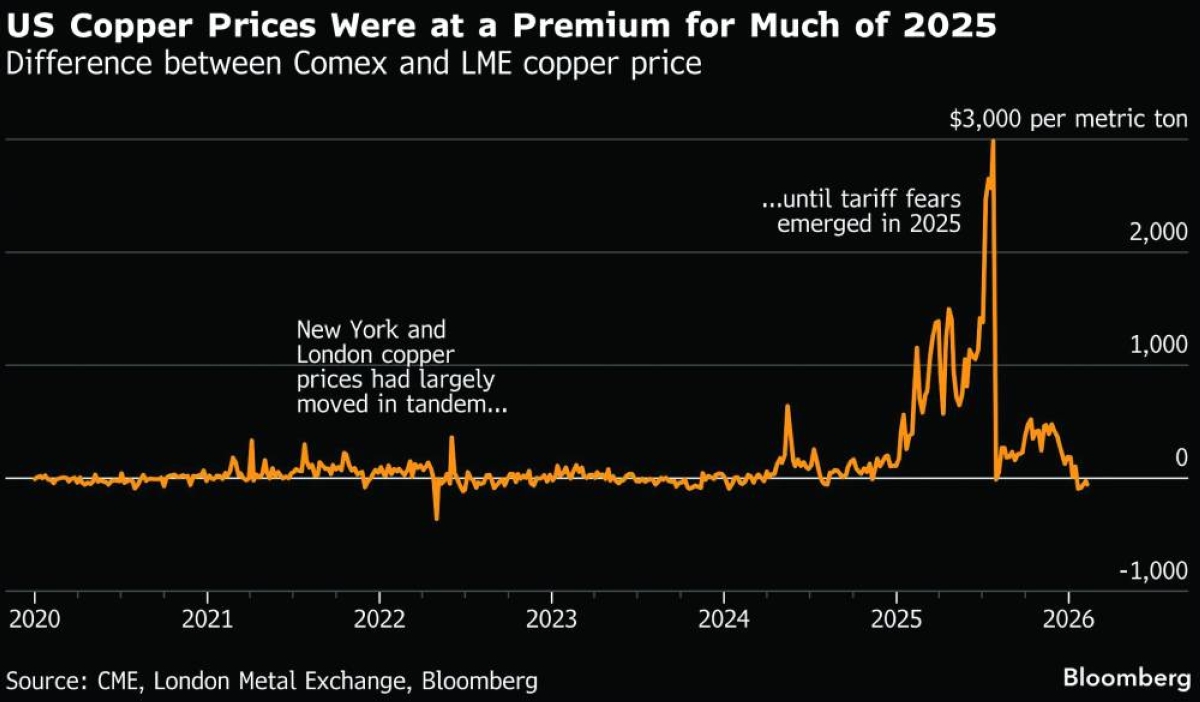
The US has quietly built up its biggest stockpile of copper in decades, distorting flows of the red metal to the rest of the world.The influx of copper into American inventories has gathered momentum over the past year and added to upward pricing pressures. The higher prices have reverberated across the copper supply chain. Why has so much copper been flowing to the US?President Donald Trump’s tariff agenda has been looming over the copper market since his return to the White House.Fears that he would impose import duties on refined copper — the most commonly traded form of the industrial metal — pushed US prices above the global benchmark set in London in the first half of last year. New York’s premium over London was so lucrative that trading houses such as Mercuria Energy Group Ltd, Hartree Partners LP and Trafigura Group raced to bring copper to US shores.The rush of transatlantic shipments temporarily slowed after Trump unexpectedly spared refined metal from the tariffs announced in July, instead imposing a 50% duty on semi-finished copper products, such as pipes and wires, and so-called derivative products, which include electrical components.However, Trump said he’d revisit the decision in the second half of this year, renewing concerns about tariffs on commodity-grade forms of copper. The profitable New York-London price gap, which had collapsed in July, was revived and US inventories continued to swell.The country imported 1.7mn metric tonnes of copper last year, according to the US Geological Survey, almost double the volume from a year earlier. How big is the US copper stockpile?Copper held in secure, exchange-approved warehouses that back futures contracts traded on the CME’s Comex have been on a relentless upswing since early 2025. Comex inventories stood at 589,081 short tonnes (534,405 metric tonnes) as of February 6, a more than fivefold increase from a year prior and the highest level CME has recorded in data going back to 1989.If the metal held in off-exchange inventories is included, the total US copper hoard is around 1mn metric tonnes, BMO Capital Markets estimates. That’s roughly equivalent to how much the world’s biggest copper mine, Escondida in Chile, produces in a year. How has copper stockpiling in the US affected the global market?The copper inflows into the US have tightened supply available for the rest of the world, exacerbating the pressures from a series of mine disruptions stretching from Chile to Indonesia.These two dynamics, as well as speculative trading activity, have sent copper prices to records. Prices soared above $14,500 per metric tonne on the London Metal Exchange in late January, before taking a breather amid a broad metals selloff.Analysts at Goldman Sachs Group Inc have warned that copper prices have overshot fundamentals. BNP Paribas SA strategist David Wilson said in February that the metal is “still overvalued” and levels above $11,000-11,500 a tonne are “almost entirely speculatively driven”.The elevated copper prices have taken a toll on fabricators in China — the world’s biggest copper consumers — who shape the metal into wire, tubes and foil for manufacturers and have struggled to pass on their higher feedstock costs to customers. Many Chinese copper plants are expected to take longer breaks from production over the Lunar New Year holiday as near-record prices chill industrial demand for the metal.While there’s long-term optimism about rising copper usage for renewable energy technology, electric vehicles and data centres for artificial intelligence, the soft near-term demand outlook is reflected in stockpiles at exchange warehouses in London, Shanghai and New York, which have reached their highest level since 2003. What could happen to the giant US copper stockpile?Analysts and traders initially feared that the copper accumulated in the US would flood the global market and depress prices if the refined metal escaped Trump’s tariffs.More recently, views have shifted toward a large — or even larger — stockpile enduring as companies and the government look to protect the country’s manufacturing base from scarce supply, volatile prices and overreliance on imports from China. That sentiment has been underpinned by the Trump administration’s plans to create a $12bn stockpile of critical minerals, known as “Project Vault,” via a public–private partnership.It’s unclear how much of Project Vault will be dedicated to copper, which is one of 60 minerals the US government considers to be “critical” and at high risk of supply chain disruption. Mining billionaire Robert Friedland, who was present at the Oval Office launch of Project Vault in early February, said the red metal would undoubtedly be included.“The thrust of this argument is the notion that the copper stock build we are witnessing today could be not just commercial in nature but government driven too,” BMO analysts wrote in a January report. Is there precedent for the US amassing large amounts of copper?The BMO report said that “compared with other periods in history that were witness to major geopolitical upheavals, today’s inventory still does not look so dramatic.”During the Cold War, the US stockpiled minerals to try to ensure enough supply during a multi-year conflict with the Soviet Union. It held 10 months worth of copper consumption in the early 1960s. The 1mn tonnes of the red metal currently sitting in the US is enough to meet about seven months of demand, according to BMO estimates. Is there enough warehousing space in the US for all this copper?Yes. The CME added 649,979 short tonnes of copper warehousing capacity in the US last year, taking the total to a little over 1.1mn short tonnes spread across seven states: Arizona, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Michigan, Texas and Utah.Meanwhile, warehouse firms are still applying to provide additional space to store copper at CME-approved locations. Henry Bath LLC, for example, applied in January to host warehousing capacity in Cartersville, Georgia, for copper deliverable against the Comex copper futures contract. If approved, this would be a new location for the Comex-registered copper warehousing network.
Thursday, February 12, 2026
|
Daily Newspaper published by GPPC Doha, Qatar.