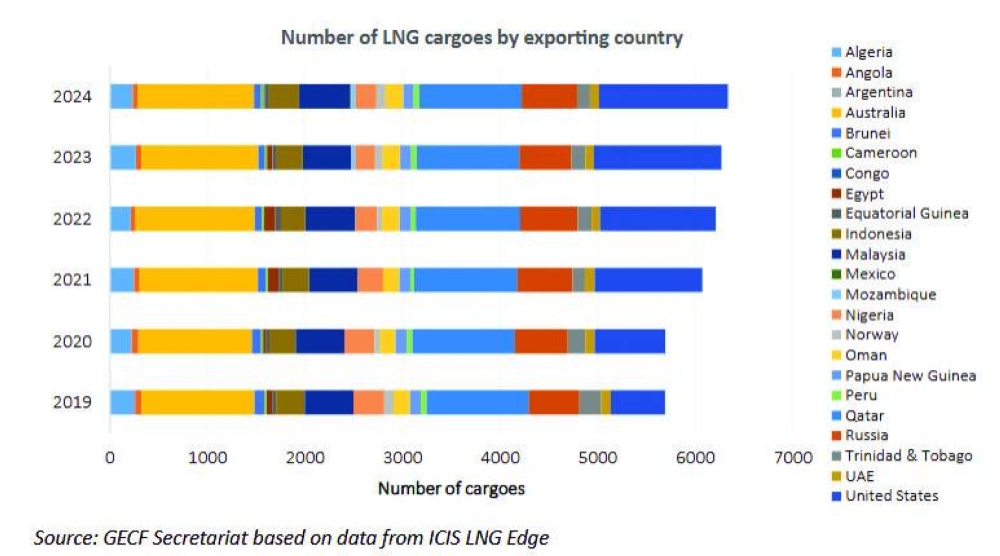
Qatar, US and Australia have delivered over 1,000 LNG shipments each in 2024, a new report by GECF has shown.
These three top LNG exporters accounted for 56% of the global LNG shipment, according to 'GECF Annual Gas Market Report 2025'.
The number of LNG shipments increased by 1%, adding 66 cargoes, to reach a total of 6,336 cargoes in 2024, the report said.
Although the number of LNG shipments have been consistently increasing in recent years, the past three years marked a slowdown in the growth rate of the sector, following the 7% expansion in 2021.
GECF members made up six of the top ten exporters: Qatar, Russia, Malaysia, Algeria, Nigeria and Trinidad & Tobago.
Together, GECF countries were responsible for 48% of all LNG cargoes exported globally.
New entrants to the LNG shipping sector, namely Congo and Mexico, delivered 14 LNG cargoes.
Indonesia exported 45 more cargoes than the previous year, marking a 17% increase.
Russia followed with a 7% rise, or 36 more cargoes, reflecting its efforts to diversify gas exports.
Mozambique saw the largest percentage increase at 24%, adding nine cargoes as it ramped up its export operations.
Looking ahead to 2025, the number of LNG shipments is expected to rise, driven by increased LNG exports, new export facility startups, ramped-up supply from existing producers, and new market entrants like Canada, Mauritania and Senegal.
LNG shipping cost:
New carrier additions have prompted a loosening of the global LNG shipping market, GECF noted,
LNG shipping costs depend on three key factors, in particular the cost of chartering the LNG carrier, shipping fuel expenses, and the distance between the loading and receiving ports.
The year 2024 proved to be exceptional for the LNG shipping market, as the average annual spot charter rate for steam turbine LNG carriers plummeted to a record low of $25,000/day, down from $43,000/day in 2020, $65,000/day in 2021, $72,000/day in 2022 and $53,000/day in 2023.
Similar declines were seen across other segments of the global LNG carrier fleet.
The average spot charter rate for TFDE carriers was $40,000/day, while two-stroke carriers averaged $55,300/day—53% and 49% lower than the five-year average, respectively.
Spot charter rates were notably atypical in 2024, the report said.
Typically, charter rates follow a seasonal pattern, remaining stable during periods of regular LNG demand and rising in Q4 as Europe and
Asia compete for cargoes ahead of the winter season.
However, in 2024, rates declined from August onward, reaching an average low of $6,400/day in December, the report said.
The decline in spot charter rates was driven by three main factors. Firstly, the LNG shipping market experienced a record-breaking expansion of the carrier fleet, with the number of newly commissioned vessels reaching 70 and with the rate of these additions significantly outpacing the growth of global LNG export capacity.
Secondly, many of these newly commissioned LNG carriers were initially ordered for long-term charter contracts linked to upcoming liquefaction projects.
However, due to the common practice of commissioning vessels before the commercial operations of LNG liquefaction plants commence, coupled with delays in the startup of some projects, many of these carriers have been temporarily redirected to the spot charter market. Thirdly, the decline in LNG cargoes used for floating storage contributed to the slump in spot charter rates in Q4, 2024.
Floating storage was nearly non-existent in Europe in Q4, 2024, compared to around 20 carriers used for floating storage in Europe in Q4, 2023, GECF said.
Business
Qatar, US and Australia deliver over 1,000 LNG shipments each in 2024: GECF
These three top LNG exporters accounted for 56% of the global LNG shipment, according to 'GECF Annual Gas Market Report 2025'
Qatar, US and Australia have delivered over 1,000 LNG shipments each in 2024, a new report by GECF has shown.

