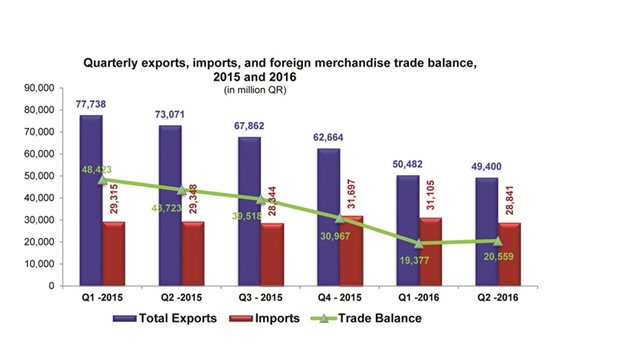
Qatar’s foreign trade surplus rose 6% quarter-on-quarter (q-o-q) to QR20.56bn in the second quarter (Q2) of 2016 as imports fell faster than exports, according to official figures.
Although on year-on-year (y-o-y), trade surplus more than halved from QR43.72bn in Q2 of 2015; Asia remained the largest trading partner, according to the Ministry of Development Planning and Statistics.
In Q2 2016, Qatar’s total exports (including re-exports) fell 32.4% y-o-y to QR49.4bn, dragged down by mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials (34.9%), chemicals and related products (25.4%), and manufactured goods (27.3%). However q-o-q, Qatar’s export decline was only 2.1%.
In Q2 2016, Qatar’s imports were QR28.8bn, showing a y-o-y 1.7% fall, mainly on machinery and transport equipment (10.5%), and manufactured goods (6.4%). However, imports fell 7.3% against Q1 2016.
Asia was the principal destination of Qatar’s exports and imports, representing 70.8% and 30.7% respectively during Q2, 2016.
Japan’s exports were QR8.9bn (17.9% of total), followed by South Korea QR7.7bn (15.7%), and India QR6.1bn (12.4%).
On the other hand, China was the principal origin of imports with QR3.3bn (11.4% of total), followed by Japan QR1.7bn (5.8%) and India QR1.1bn (3.8%).
The trade balance with this economic area was QR26.1bn, while total trade (i.e. exports plus imports) amounted to QR43.9bn.
Exports to Asia were mainly liquefied natural gas (LNG), crude oil, condensates, propane, butane, naphtha, polyethylene, aluminium alloys, urea, methanol, polyethylene, and vinyl chloride.
Imports comprised principally vehicles, telephones for cellular networks, semi-milled or wholly milled rice, whether or not polished or glazed, electric cables, air conditioning machines, tubes, pipes, drilling machinery for oil wells and gold jewellery.
The European Union (EU) constituted 11.8% of Qatar’s exports and 30.7% of Qatar’s imports. The UK reported exports of QR2.1bn (4.2% of total), Italy QR1bn (2%) and Belgium QR0.7bn (1.4%); while imports from Germany were QR3bn (10.3% of total), Italy QR1.3bn (4.4%) and the UK QR1.2bn (4.2%).
In Q2 2016, the trade balance with the EU showed a deficit of QR3bn, while total trade amounted to QR14.7bn.
Exports to the EU were mainly LNG, polyethylene, halogenated olefins, helium, aluminium alloys and biodegradable bags and sacks.
Imports included vehicles, parts of airplanes or helicopters, medical solutions, parts for turbo jets or turbo propellers, tubes, pipes, centrifugal pumps and drilling machinery for oil wells.
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) accounted for 9.8% of Qatar’s exports and 17.3% of imports. In the GCC, the UAE was the first partner country reporting exports of QR3.4bn (6.9% of total) and imports of QR2.8bn (9.8% of total). The trade balance with the GCC registered a deficit of QR0.2bn, while total trade was QR9.8bn. Exports to GCC countries comprised LNG, condensates, polyethylene, jet fuel, ether derivatives, sheet piling of iron and steel, rails and diesel for engines.
Imports included pebbles, gravel, broken or crushed stone, camels, iron ores, copper wires, gold jewellery, ethylene, electric cables, yogurt and vegetable fats and oils and their fractions.
In Q2 2016, surpluses were registered with other Arab countries, QR0.8bn (3.9%) and non-Arab African countries QR0.4bn (2%). A deficit was seen with the US of QR2.8bn and with Other European countries (not in the EU) of QR0.6bn.
QATAR

