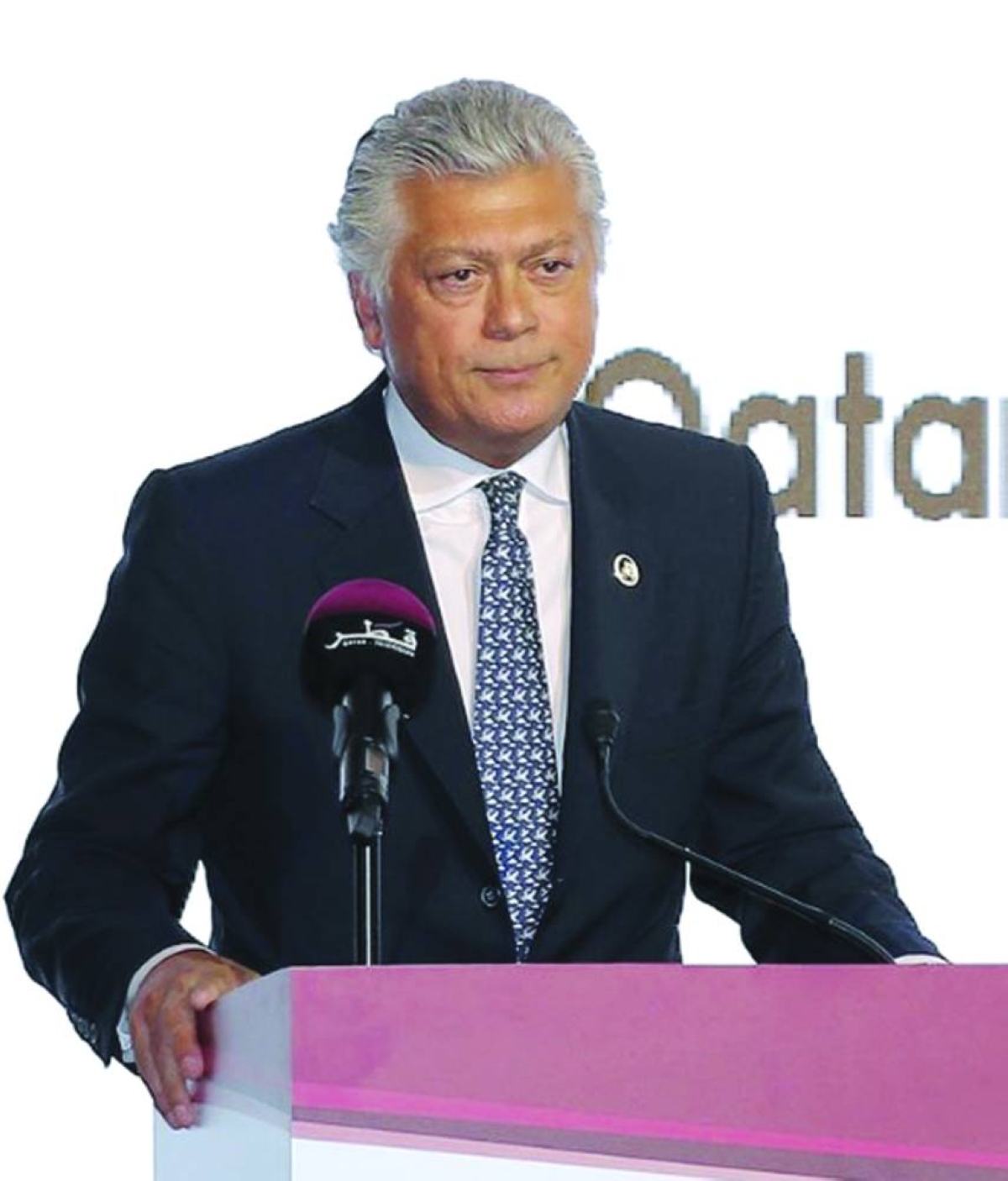
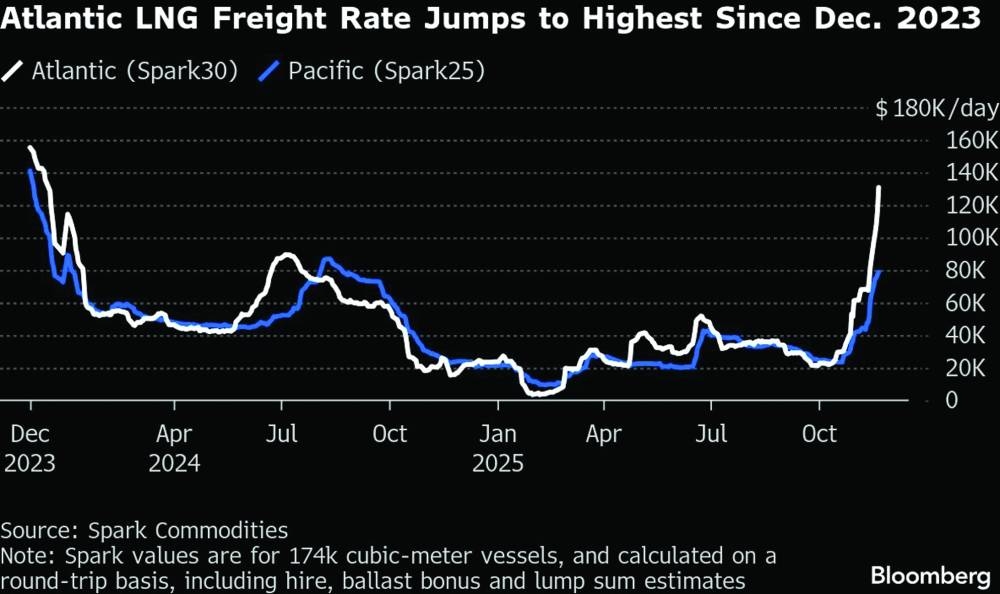
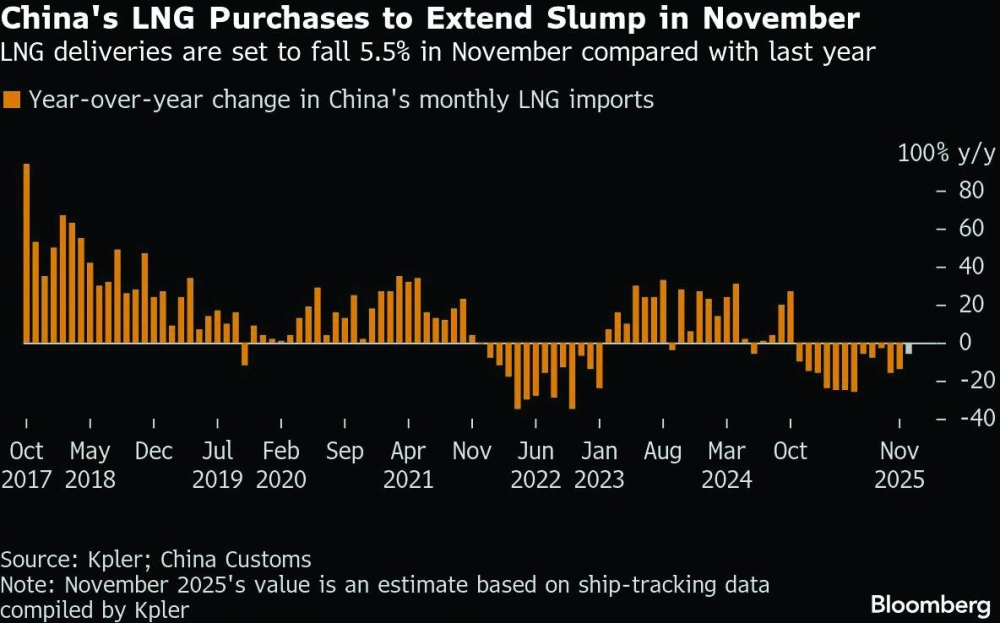
Qatar’s global LNG strength and Greece’s role as Europe’s energy gateway are converging into a partnership that will define energy resilience and regional connectivity in 2026 and beyond, an official of the Greece-Qatar Business Council & Friendship Committee has said.Panagiotis G Mihalos, the committee’s founder and chairman, said the complementarity between Qatar’s reliability as a source of liquefied natural gas and Greece’s infrastructure, including LNG/FSRU terminals and interconnectors, offers Europe a more diversified and resilient energy architecture.“There is a natural complementarity. Qatar is a global leader in LNG, offering reliability and long-term strategic vision. Greece, meanwhile, has emerged as a critical gateway for energy into Europe, particularly through LNG/FSRU terminals and regional interconnectors. In addition, through IMEEC, our cooperation can expand, in the future, to electricity or even hydrogen,” Mihalos told Gulf Times in an exclusive interview.Mihalos, who is also founder and president of the Georgios M Mihalos Foundation and the Nisyros Dialogues – Bridging the East Med, pointed to the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) as a framework where Qatar can act as both an energy and logistics hub.“Corridors are not just physical routes; they are corridors of trust, and Qatar understands this better than most,” he emphasised.Mihalos outlined three levels of co-operation: strategic energy partnerships, joint infrastructure investments, and knowledge exchange on resiliency and sustainability. At the same time, he proposed institutionalising an annual Greece-Gulf strategic dialogue on energy security and connectivity, linking policymakers, industry leaders, and thinkers.Looking ahead, Mihalos pointed out that the partnership must evolve into a long-term institutional presence. “We intend to institutionalise this co-operation. Not as a one-off presence, but as a long-term partnership with the Doha Forum and Qatari institutions,” said Mihalos, who was in Qatar and participated in the Doha Forum.Mihalos said he sees Qatar as a trusted bridge-builder in energy and diplomacy, particularly at moments when traditional diplomacy struggles. “Qatar’s credibility, patience, and commitment to a peaceful mediation position make it a stabilising force across regions,” Mihalos explained.Asked if he were to design a Qatar-focused dialogue under his foundation, Mihalos said he would prioritise peace mediation, energy transition and connectivity, the role of culture in diplomacy, strategic migration governance, and environmental resilience. He highlighted water management as a shared challenge between island ecosystems, such as Nisyros, and arid environments, like Qatar, suggesting the exchange of knowledge on sustainability.He also underscored the importance of embracing the digital frontier: “We must address digital diplomacy and the ethics of artificial intelligence as technology is rapidly reshaping geopolitical dynamics. Understanding the intersection of innovation and statecraft is crucial, as we aim to ensure that emerging technologies serve as bridges for co-operation rather than instruments of division,” Mihalos stressed.He added that the dialogues must focus on moving from crisis management to co-operative foresight: “Ultimately, that is the shared philosophy of Qatar, the Doha Forum, and the Nisyos Dialogues.”
Tuesday, February 10, 2026
|
Daily Newspaper published by GPPC Doha, Qatar.