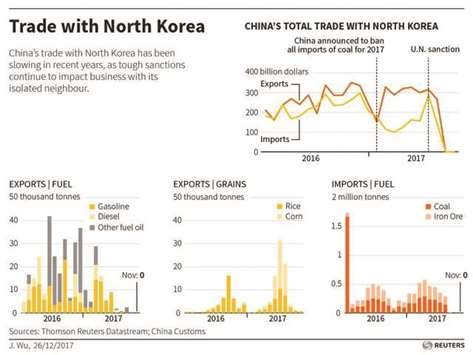
China exported no oil products to North Korea in November, Chinese customs data showed, apparently going above and beyond sanctions imposed earlier this year by the United Nations in a bid to limit petroleum shipments to the isolated country.
Tensions have flared anew over North Korea’s ongoing nuclear and missile programmes, pursued in defiance of years of UN resolutions.
Last week, the UN Security Council imposed new caps on trade with North Korea, including limiting oil product shipments to just 500,000 barrels a year.
Beijing also imported no iron ore, coal or lead from North Korea in November, the second full month of the latest trade sanctions imposed by UN.
China, the main source of North Korea’s fuel, did not export any gasoline, jet fuel, diesel or fuel oil to its isolated neighbour last month, data from the General Administration of Customs showed yesterday.
November was the second straight month China exported no diesel or gasoline to North Korea.
The last time China’s jet fuel shipments to Pyongyang were at zero was in February 2015. “This is a natural outcome of the tightening of the various sanctions against North Korea,” said Cai Jian, an expert on North Korea at Fudan University in Shanghai.
The tightening “reflects China’s stance”, he said.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Hua Chunying said she didn’t know any details about the oil products export situation. “As a principle, China has consistently fully, correctly, conscientiously and strictly enforced relevant UN Security Council resolutions on North Korea.
We have already established a set of effective operating mechanisms and methods,” she said at a regular briefing yesterday, without elaborating.
Since June, state-run China National Petroleum Corp (CNPC) has suspended sales of gasoline and diesel to North Korea, concerned that it would not get paid for its goods, Reuters previously reported.
Beijing’s move to turn off the taps completely is rare.
In March 2003, China suspended oil supplies to North Korea for three days after Pyongyang fired a missile into waters between the Korean Peninsula and Japan. It is unknown if China still sells crude oil to Pyongyang.
Beijing has not disclosed its crude exports to North Korea for several years.
Industry sources say China still supplies about 520,000 tonnes, or 3.8mn barrels, of crude a year to North Korea via an ageing pipeline.
That is a little more than 10,000 barrels a day, and worth about $200mn a year at current prices.
North Korea also sources some of its oil from Russia. Chinese exports of corn to North Korean in November also slumped, down 82% from a year earlier to 100 tonnes, the lowest since January.
Exports of rice plunged 64% to 672 tonnes, the lowest since March.
Trade between North Korea and China has slowed through the year, particularly after China banned coal purchases in February.
In November, China’s trade with North Korea totalled $388mn, one of the lowest monthly volumes this year.
China has renewed its call on all countries to make constructive efforts to ease tensions on the Korean peninsula, urging the use of peaceful means to resolve issues.
But tensions flared again after North Korea on November 29 said it had tested a new intercontinental ballistic missile that put the US mainland within range of its nuclear weapons.
Meanwhile Chinese exports of liquefied petroleum gas to North Korea, used for cooking, rose 58% in November from a year earlier to 99 tonnes.
Exports of ethanol, which can be turned into a biofuel, gained 82% to 3,428 cubic metres.
.
