By Dr Antony Joseph George
Chickenpox is a viral infection caused by varicella virus, and results in eruptions mainly over body and head. It is highly contagious which spreads from person to person through air. Although usually it falls in the category of mild diseases, at times it can cause serious complications.
Infection period
A person is infective from 48 hours before the appearance of rashes, until all the lesions become scales. Varicella virus can spread through air, by direct contact with the rash, and even by droplets of saliva during coughs or sneezing. The infection lasts in children for 14-16 days.
Geographical variation
In countries where paediatric immunisation is introduced, the incidence of chickenpox is low. However, in countries like Qatar, where majority of the population are expatriates, chances of chickenpox are relatively higher. The pool of residents from countries around the world also brings in infected people. Many of the residents are also not vaccinated on a routine basis before they come to Qatar. This results in higher incidence rate of chickenpox among foreign population. Countries in tropical and sub-tropical regions also tend to depict higher rate of chickenpox incidence.
Consultation
When you suspect that you have chickenpox symptoms as mentioned above consult your doctor immediately. The doctor will prescribe medicines which are effective against the virus. This treatment will lessen the severity of the disease and help in preventing complications. The below mentioned symptoms require immediate consultation:
Rashes in eyes
Skin rashes become painful, swollen and very red, indicating bacterial infection
Dizziness
Disorientation
Breathing problems
Ongoing immune deficiency (ongoing treatment with chemotherapy or steroid injections).
Risk factors
If not infected with chickenpox till date
If you have not had chickenpox vaccination
Complications
Chickenpox in majority of the cases is a mild disease. But in a few cases, it may result in major complications, leading to permanent disabilities, or even death of the patient. Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) and excessive bleeding are also rare complications as a result of this disease.
(a) Bacterial infection of skin lesions and in a few cases can worsen to septicemia (blood stream infection).
(b) Pneumonia can be a complication.
(c) Infection of the brain (encephalitis).
(d) People taking chemotherapy, steroids and aspirin on regular basis have more chances of complications.
(e) New-born babies, senior citizens and pregnant women also have a higher risk of complications.
Pregnancy
Apart from risk of regular complications, chickenpox infection in pregnant ladies can also result in complications during delivery, and low weight of new-born baby, especially if infected during early stages of pregnancy. If the mother is infected with chickenpox even right after the delivery, it can lead to life-threatening situations for the newborn as well.
Chickenpox and herpes zoster
After a chickenpox infection, some patients in later life can develop a condition known as herpes zoster. This is due to reactivation of the same virus which has remained in your cells after the initial infection. It may result in blisters in the path of the nerves in any part of the body. This condition can cause immense pain during illness, and few patients may even have post-hepatic neuralgia (pain persisting for long time in the area of eruption). A vaccination is also available to prevent herpes zoster. Lab tests are not usually required for diagnosis when the eruptions are typical. But in case of doubt, chickenpox can be confirmed with the help of blood tests and culture from skin lesions.
Treatment
In healthy children, it is very mild and requires no specific treatment. But in adults a drug, which is anti-viral called acyclovir, is given. If given early in the course of illness, acyclovir can shorten the duration and may prevent development of complications.
Self-care measures
Do not scratch as this may cause secondary bacterial infection. The scratches may leave scars and this may have bad cosmetic effects, especially on the face.
Calamine lotion may be smoothening. Paracetamol can be given for fever and pain. When you get vaccinated you protect yourself, and others from the disease, as you will not be a source of infection for other people.
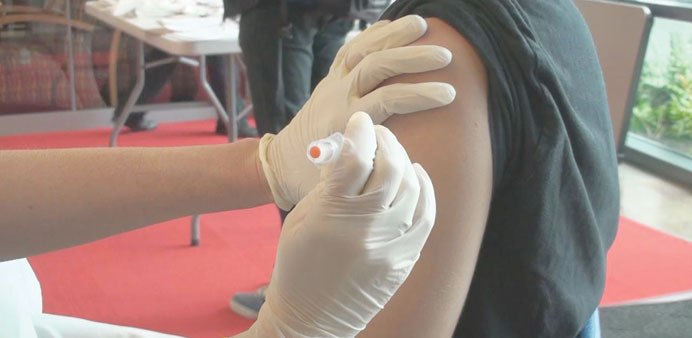
Prevention
Vaccination is the best way to prevent chickenpox. As much as 98% of the people who receive the vaccination are protected. If chickenpox occurs in vaccinated people, the disease may be less severe.
In children, two doses of vaccination will be required: 1st dose between 12 and 15 months. Second dose should be administered between 4 to 6 years of age. Older children who have not received the vaccination may receive two catch-up doses three months apart. Adults who have not received the vaccination or have not been infected with chicken box, can take 2 catch-up doses of vaccination with an interval of four to eight weeks apart.
Chickenpox vaccination is not administered for pregnant women. If you are planning to become pregnant, consult your doctor regarding the vaccination requirement. Women should not get pregnant for one month after getting the chickenpox vaccination. Those who are taking steroid treatment or chemotherapy for cancer should check with their doctor before getting vaccinated.
Vaccination is important for …
Healthcare professionals, especially who take care of people with weak immune system, eg HIV patients
Teachers
Childcare workers
Military personnel
Women with child bearing age
International travellers
Getting vaccination after exposure
You should get the vaccination within three-five days of being exposed. Need to take two doses -- this may either prevent the disease or make it far less severe. It will also protect you from chickenpox in future as well.
Pregnant women without immunity to chickenpox, who are exposed to chickenpox, newborns whose mothers were exposed to chickenpox five days before or two days after delivery, may receive Varicella immunisation to get protection from developing chickenpox.
Acyclovir treatment is advised for people in the house of a chickenpox patient. This is especially for those with chronic lung disease, and patients on steroid or aspirin therapy.
(Dr Antony Joseph George is a general practitioner (GP) at Aster Medical Centre- Al Hilal)