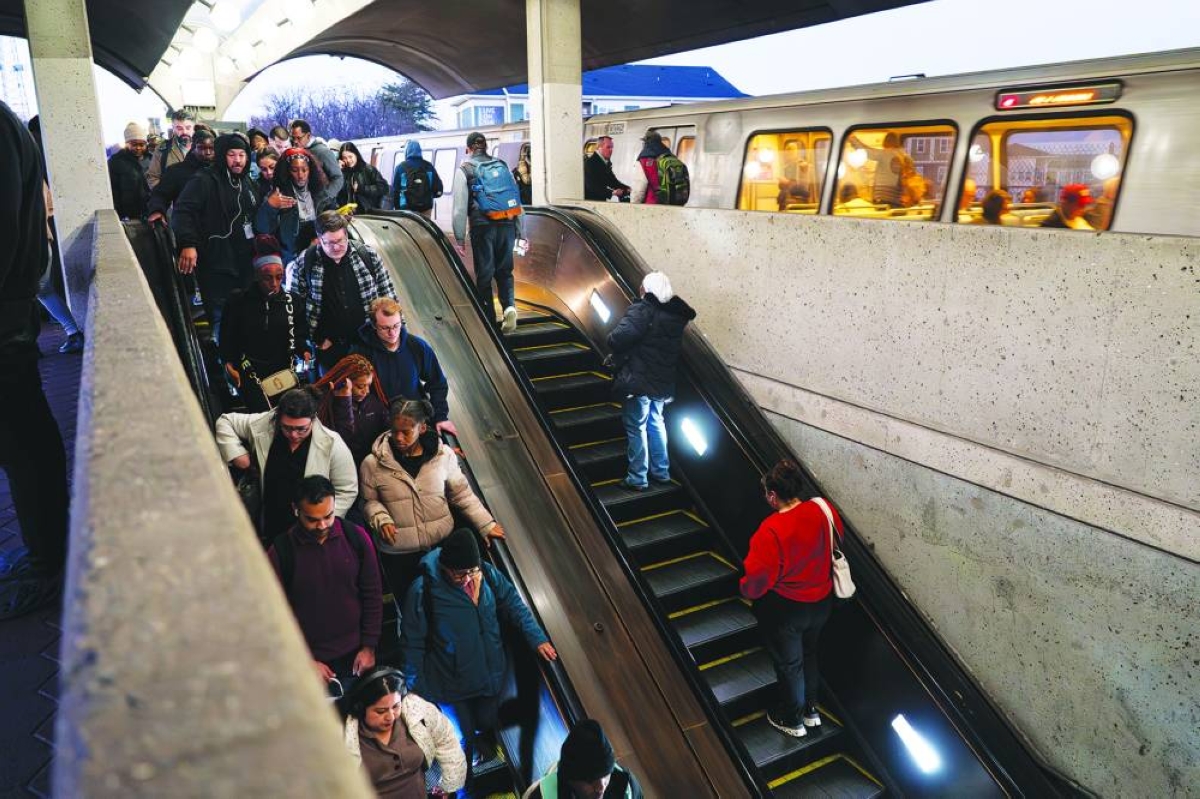
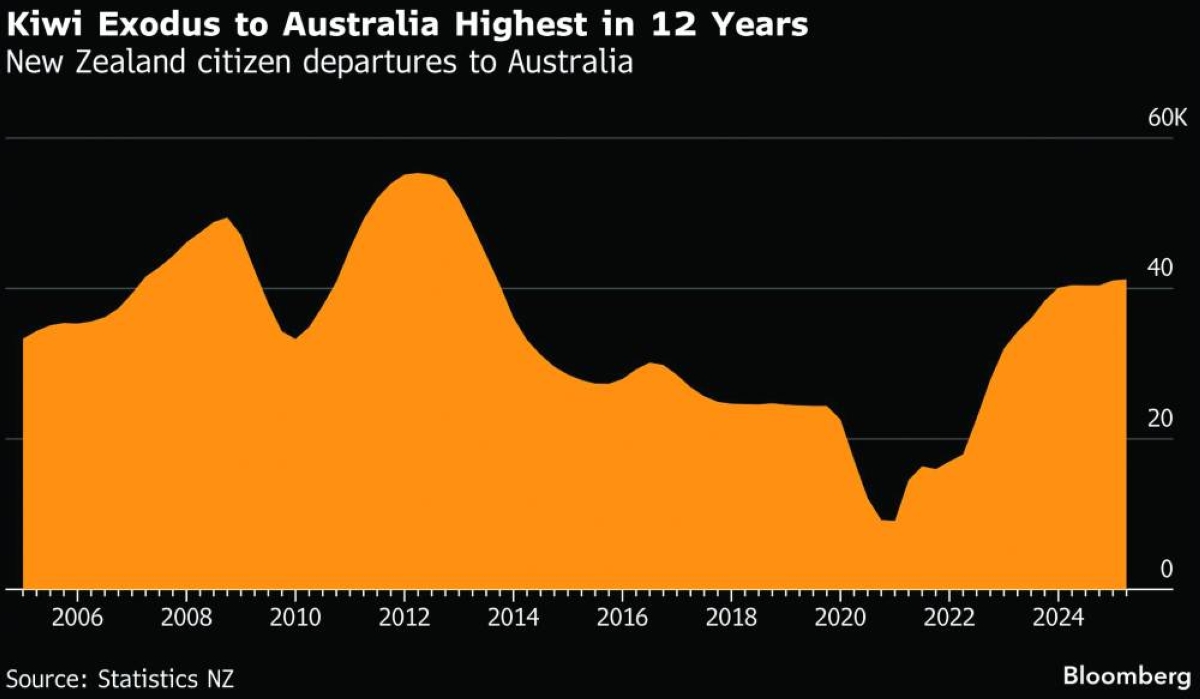
For decades, moving “across the ditch” to Australia has been an easy option for New Zealanders seeking higher pay and broader prospects. There’s no visa required and it’s just a quick, three-hour flight separating the two countries.The steady flow — joked about in the late 1970s by then-New Zealand Prime Minister Robert Muldoon as “raising the average IQ of both countries” — has recently struck a nerve due to the high number of departures and news that former Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern has become the latest high-profile Kiwi to relocate.Emigration is now feeding debate ahead of New Zealand’s November general election over wages, opportunity and what a sustained exodus might mean for the county’s long-term prospects. How significant is the exodus?The number of New Zealanders moving to Australia is at its highest level in 12 years, at about 41,000 people last year.Departures to Australia averaged about 37,000 annually between 2005 and 2019, before dropping below 17,000 in 2021, when pandemic border closures curbed travel. The recent figure is still below the 2012 peak, when more than 55,000 New Zealanders left for Australia.Statistics New Zealand estimates that more than half of citizens who leave the country are aged 20 to 39. While official data doesn’t break down destinations by age, Australia has long been popular among younger New Zealanders seeking higher wages and a larger job market. In the last few years, the flow has included not only younger people but workers of all ages particularly in the technology and finance sectors, as well as police officers, nurses and tradespeople.Even so, departures remain small relative to New Zealand’s 5.3mn population. The country still attracts more people than it loses, with a net migration gain of 14,200 in 2025. That said, it was the smallest annual net gain since 2013, excluding 2021, when pandemic border closures affected migration. What’s driving the exodus to Australia?Australia is by far the top destination for New Zealand migrants, with higher pay and stronger career prospects a major draw. Of the 67,800 citizens who left in the 12 months through June, about 61% headed across the Tasman Sea.The wage gap is significant. Average weekly ordinary-time earnings in Australia are A$2,051, compared with NZ$1,681 in New Zealand — about A$1,425 at current exchange rates. On that basis, workers can earn roughly 44% more in Australia.The gap extends beyond wages. New Zealand’s youth unemployment rate was 13.2% in the fourth quarter of 2025, compared with 9.5% in Australia in December. With a much larger population and economy, Australia also offers a broader range of jobs and, in some cases, faster career progression.Australia’s government has actively targeted New Zealand workers, running recruitment campaigns in sectors such as healthcare, early childhood education, and policing and prison services, often sweetened with higher wages and relocation packages. Kiwi arrivals have helped ease Australia’s skills shortages, but the outflow has left some essential services in New Zealand, including hospitals, understaffed. How do Australia’s and New Zealand’s economies compare?Australia’s economy is more than six times the size of New Zealand’s in nominal gross domestic product terms, and its labor force of roughly 15mn people is more than five times larger. The scale and diversity translate into a broader range of jobs and generally higher pay for those willing to relocate.Both economies are expanding, with Australia’s growing a robust 2.6% in 2025 from a year earlier. New Zealand’s economy is projected to grow around 2%.But, there is more optimism for New Zealand’s economy in 2026. The central bank expects to hold interest rates steady for much of the year and forecasts growth accelerating toward 3%. In Australia, by contrast, the Reserve Bank raised interest rates in February and is tipped to do so again in the near future, a move likely to keep growth at or below 2% this year.New Zealand’s labor market remains weak, with unemployment at a 10-year high of 5.4%. While that rate is expected to ease as business investment picks up, it is unlikely to approach Australia’s level anytime soon. Australia’s jobless rate was 4.1% in January and hasn’t been above 5% since 2021. What does the exodus mean for New Zealand?Emigration has become a major political issue ahead of the country’s November 7 general election.Opposition leader Chris Hipkins has seized on the departures, tying them to high living costs and limited opportunity at home. In a recent State of the Nation address, he said about 2,000 New Zealanders leave the country each week “because they can’t see a future here.”“Young professionals. Nurses. Teachers. Tradies who should be building homes here... they all say the same thing: ‘I love New Zealand. I want to raise a family here. But I can’t get ahead here. I can’t afford a house. I can’t find the jobs that I am trained for,’” he said, adding that almost 240,000 people have left the country in the last two years.Beyond politics, there are potential economic consequences. A sustained outflow can weigh on domestic spending, reduce the available workforce and dampen housing activity. What does the influx of New Zealand migrants mean for Australia?The inflow has provided Australia with a timely boost to its labor force amid acute worker shortages. New Zealanders have helped fill vacancies quickly in construction, healthcare and other service industries.The trans-Tasman flow is economically efficient, according to economists. It expands the workforce quickly without the administrative delays and settlement costs associated with other skilled-migration programs, and shared professional standards mean many qualifications transfer easily.One area under strain is housing. New arrivals add to rental demand, especially in Sydney, Brisbane and Perth, where vacancy rates are low and homebuilding has lagged population growth. Even if migrants help increase labor supply, the housing market can’t respond quickly with new homes, reinforcing near-term pressure on rents and prices.From a fiscal standpoint, most New Zealand migrants are young and employed, meaning they typically pay more in taxes than they receive in government benefits over time. But supporting a larger population requires upfront spending on schools, hospitals and transport, fueling debate over whether growth is stretching public services faster than they can expand.One recurring political concern in Australia is that the trans-Tasman arrangement allows migrants from third countries to use New Zealand as a “back door” to access Australia, its citizenship and welfare system. While data show that many New Zealand citizens who later settle in Australia were born overseas, there is no credible evidence that people are migrating to New Zealand with the primary intent of circumventing Australia’s migration rules.